This post was originally published on this site
For nearly 650 years, the fortress walls in the Chinese city of Xi’an have served as a formidable barrier around the central city. At 12 meters high and up to 18 meters thick, they are impervious to almost everything — except subatomic particles called muons.
Now, thanks to their penetrating abilities, muons may be key to ensuring that the walls that once protected the treasures of the first Ming Dynasty — and are now a national architectural treasure in their own right — stand for centuries more.
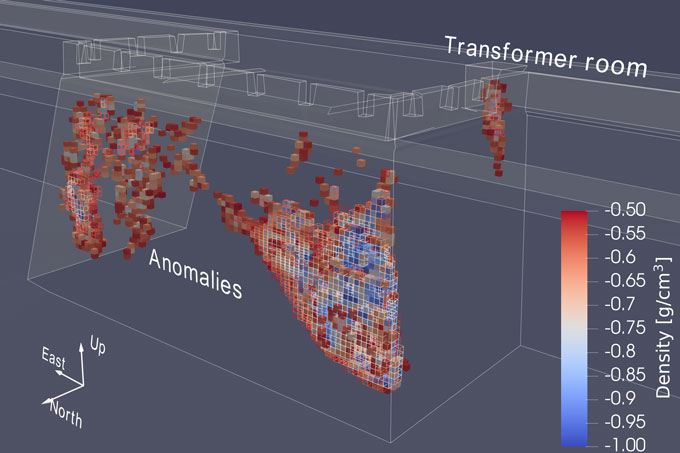
A refined detection method has provided the highest-resolution muon scans yet produced of any archaeological structure, researchers report in the Jan. 7 Journal of Applied Physics. The scans revealed interior density fluctuations as small as a meter across inside one section of the Xi’an ramparts. The fluctuations could be signs of dangerous flaws or “hidden structures archaeologically interesting for discovery and investigation,” says nuclear physicist Zhiyi Liu of Lanzhou University in China.
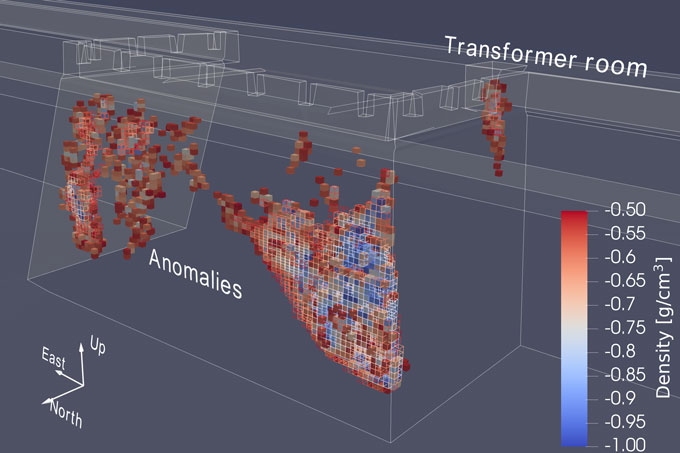
Muons are like electrons, only heavier. They rain down all over the planet, produced when charged particles called cosmic rays hit the atmosphere. Although muons can travel deep into earth and stone, they are scattered or absorbed depending on the material they encounter. Counting the ones that pass through makes them useful for studying volcano interiors, scanning pyramids for hidden chambers and even searching for contraband stashed in containers impervious to X-rays (SN: 4/22/22).
Though muons stream down continuously, their numbers are small enough that the researchers had to deploy six detectors for a week at a time to collect enough data for 3-D scans of the rampart.
It’s now up to conservationists to determine how to address any density fluctuations that might indicate dangerous flaws, or historical surprises, inside the Xi’an walls.